C program for kruskal’s algorithm
It is an
algorithm for finding the minimum cost spanning tree of the given graph.
In kruskal’s algorithm, edges are added to the spanning tree in increasing order of cost. If the edge E forms a cycle in the spanning, it is discarded.
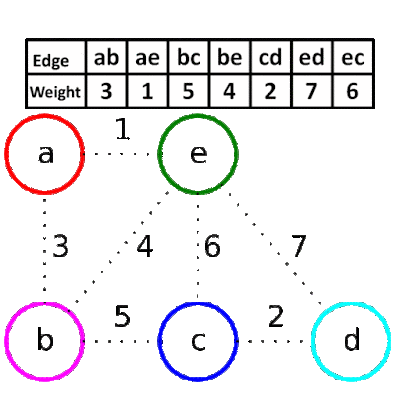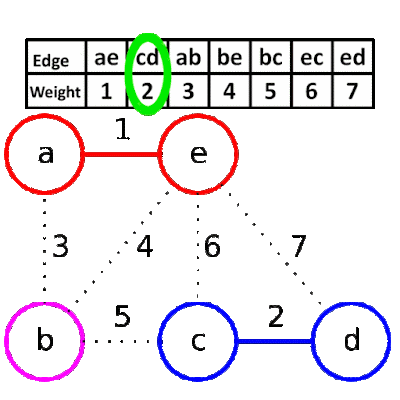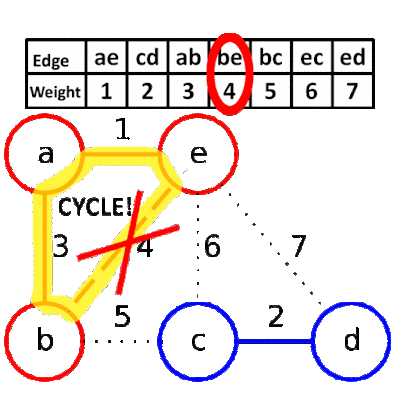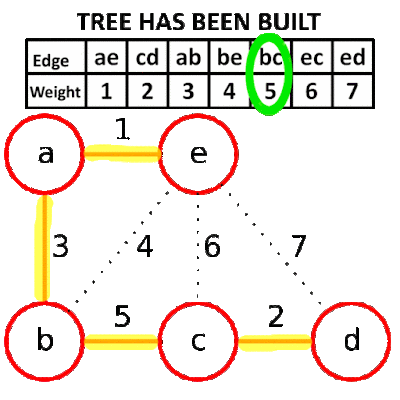
C program for constructing a minimum cost spanning tree of a graph using Kruskal’s algorithm:
Kruskal’s Algorithm
This algorithm will create spanning tree with minimum weight, from a given weighted graph.
- Begin
- Create the edge list of given graph, with their weights.
- Sort the edge list according to their weights in ascending order.
- Draw all the nodes to create skeleton for spanning tree.
- Pick up the edge at the top of the edge list (i.e. edge with minimum weight).
- Remove this edge from the edge list.
- Connect the vertices in the skeleton with given edge. If by connecting the vertices, a cycle is created in the skeleton, then discard this edge.
- Repeat steps 5 to 7, until n-1 edges are added or list of edges is over.
- Return

C program for constructing a minimum cost spanning tree of a graph using Kruskal’s algorithm:
#include<stdio.h> #define MAX 30 typedef struct edge { int u,v,w; }edge; typedef struct edgelist { edge data[MAX]; int n; }edgelist; edgelist elist; int G[MAX][MAX],n; edgelist spanlist; void kruskal(); int find(int belongs[],int vertexno); void union1(int belongs[],int c1,int c2); void sort(); void print(); void main() { int i,j,total_cost; printf("\nEnter number of vertices:"); scanf("%d",&n); printf("\nEnter the adjacency matrix:\n"); for(i=0;i<n;i++) for(j=0;j<n;j++) scanf("%d",&G[i][j]); kruskal(); print(); } void kruskal() { int belongs[MAX],i,j,cno1,cno2; elist.n=0; for(i=1;i<n;i++) for(j=0;j<i;j++) { if(G[i][j]!=0) { elist.data[elist.n].u=i; elist.data[elist.n].v=j; elist.data[elist.n].w=G[i][j]; elist.n++; } } sort(); for(i=0;i<n;i++) belongs[i]=i; spanlist.n=0; for(i=0;i<elist.n;i++) { cno1=find(belongs,elist.data[i].u); cno2=find(belongs,elist.data[i].v); if(cno1!=cno2) { spanlist.data[spanlist.n]=elist.data[i]; spanlist.n=spanlist.n+1; union1(belongs,cno1,cno2); } } } int find(int belongs[],int vertexno) { return(belongs[vertexno]); } void union1(int belongs[],int c1,int c2) { int i; for(i=0;i<n;i++) if(belongs[i]==c2) belongs[i]=c1; } void sort() { int i,j; edge temp; for(i=1;i<elist.n;i++) for(j=0;j<elist.n-1;j++) if(elist.data[j].w>elist.data[j+1].w) { temp=elist.data[j]; elist.data[j]=elist.data[j+1]; elist.data[j+1]=temp; } } void print() { int i,cost=0; for(i=0;i<spanlist.n;i++) { printf("\n%d\t%d\t%d",spanlist.data[i].u,spanlist.data[i].v,spanlist.data[i].w); cost=cost+spanlist.data[i].w; } printf("\n\nCost of the spanning tree=%d",cost); }
 |
| Output Screenshot |



era pra ter comentado, comenta aki
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDelete